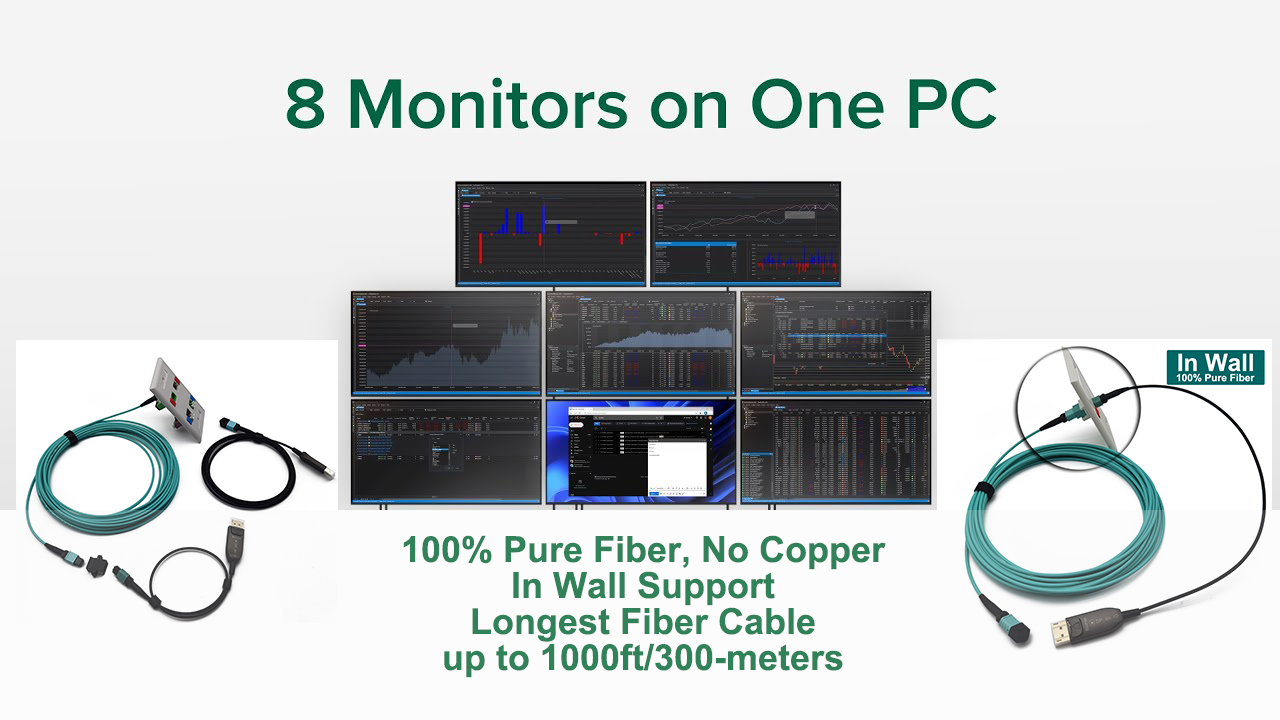
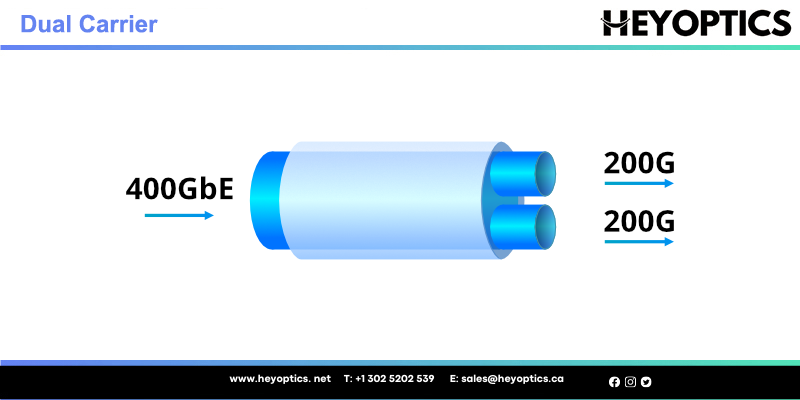
What does Dual Carrier Mean: 400G OTN Technologies
400G The opportunity of OTN technology is that PMC Digi-g4 is the highest density single-chip 4 × 100gott processor in the industry, and its port power has been reduced by more than half, which has solved the implementation requirements of encryption transmission technology supporting SDN, and met the capacity, security and flexibility of 400g line card in packet-optical transport platform (p-OTP), ROADM / WDM and optimized data center interconnection platform Please. In today's optical network connection, it is very important to provide support for the bearer network. Facing the evolution of a 400g optical network can be a situation shortly.
100G vs 400G Network
The replacement of 100g to 400g is not to replace 100g with 400g, but to use 400g inappropriate scenarios. 100g still has its advantages in the transmission performance, for example, the transmission distance is longer than 400g, so the global OTN market will maintain the coexistence of 100g and 400g for a long time.
G.654. E fiber with a large effective area and low loss is considered to be the best choice to support the next generation ultra-high-speed, long-distance, and large capacity transmission, and has become a hot topic in the industry. With the emergence of new services such as cloud computing, big data and high-definition video, as well as the upcoming trial commercial deployment of 5g services, network bandwidth pressure is increasing, and operators put forward higher requirements for single fiber capacity. Compared with the existing 100g system, 400g technology has the advantages of large bandwidth, low delay and low power consumption. It is an irresistible trend to deploy 400g system to meet bandwidth requirements.
Three transmission schemes of 400g in OTN network:
2x200g transmission scheme, 4x100g transmission scheme and 1x400g transmission scheme
Compared with the above three transmission schemes, they have their own characteristics and application scenarios. At present, the most widely used is the first 2x200g transmission scheme. The carrier and reactive power modulation of 200km-500am are realized in DMN.
We take 2x200g transmission scheme as an example to introduce the key technologies of 400g system.
PM-16qam Technology
This is a high order mode modulation scheme. PM refers to separating an optical signal into two polarization directions, and then modulating the signal to these two polarization directions for transmission. It is equivalent to the data processing of "1 divided into 2", and the rate is reduced by half.
16QAM means that one symbol represents four digital bits, which is equivalent to processing data in one part into four, and the rate is reduced by 1 / 4.
Carrier double light source technology
Single carrier only uses one frequency point; multi carrier uses several frequency points to transmit information. If N frequencies transmit information to one user, the rate can be increased by N times.
The 400g dual carrier carries out signal processing through DSP. One 400g is divided into two 200g pm-16qam signals, and one 200g occupies 37.5 GHz spectrum. In this way, 400g only needs 75 GHz spectrum and achieves the spectrum efficiency of 5.33 bit / S / Hz.
Variable Grid ROADM Technology
Flexible packaging and intelligent scheduling of optical signals on the line are realized.
A variable grid means that the channel spacing is configurable and supports intervals starting from 37.5 GHz in steps of 12.5 GHz.
The variable grid is compatible with 50 GHz and 100 GHz wavelength grids at fixed intervals.
The service board supports 12.5 GHz wavelength tuning, and the combining and splitting board supports 12.5 GHz variable grid configuration, which can be packaged flexibly according to the signal size.
The optical signal can be reconstructed by ROADM to realize the intelligent scheduling of optical signal.
What does dual carrier mean?
Dual-Carrier for 400G OTN, also named dual-wavelength 400G, offers 400G capacity via two 200G wavelengths. The dual-carrier 400G system based on the 2× 200G super-channel scheme adopts lower-order modulation formats like PM-QPSK (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying, a symbol represents two bits, which means the rate is reduced to 1/2), PM-8QAM or PM-16QAM. Dual-carrier for 400G optical transport network is applied in more complex metro networks to achieve 400G long-haul transmission.
Pros of Dual-Carrier for 400G Optical Transport Network
The spectrum efficiency of dual-carrier 400G has increased by more than 165%, with relatively high system integration, small size, low power consumption. Dual-carrier 400G is regarded as the most commonly-used technology for 400G OTN.
The span of dual-carrier 400G is longer than single-carrier 400G, which can reach up to 500km for commercial use. When deployed with low-attenuation fiber optic cable and EDFA (Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifiers), dual-carrier for 400G OTN network can cover more than 1000km, which can basically satisfy the 400G long-haul transmission application.
Cons of Dual-Carrier for 400G Optical Transport Network
Even with low-attenuation fiber optic cable and EDFA, dual-carrier 400G still fails to reach as long as quad-carrier 400G does, not suitable for ultra long-haul (ULH) transmission over 2000km.
Conclusion
In all,dual-carrier for 400G OTN network is the ideal solution for MAN transmission (with PM-16QAM) and medium long-haul transmission (with PM-QPSK);As global data traffic keeps climbing, there is no end to bandwidth demands. While it may take time to transit to 400G, you can learn about What's the Current and Future Trend of 400G Ethernet? or What is the difference between single carrier and dual carrier network? to make preparations first.