Fibre Channel Switch vs Ethernet Switch:What the difference between?
Optical fiber switch is a kind of high-speed network transmission relay equipment, also known as fibre channel switch and San switch. Compared with ordinary switch, it uses optical fiber cable as transmission medium. The advantages of optical fiber transmission are high speed and strong anti-interference ability.There are mainly two kinds of optical switch, one is used to connect the FC switch of storage. The other is Ethernet switch, the port is optical fiber interface, and the appearance of ordinary electrical interface is the same, but the interface type is different.
What Is Fibre Channel Switch?
Fibre Channel (FC), designed for storage area networks (SANs), is a high-speed network technology used to connect computer data storage to servers, providing point-to-point, switched and loop interfaces to deliver in-order and lossless raw block data.
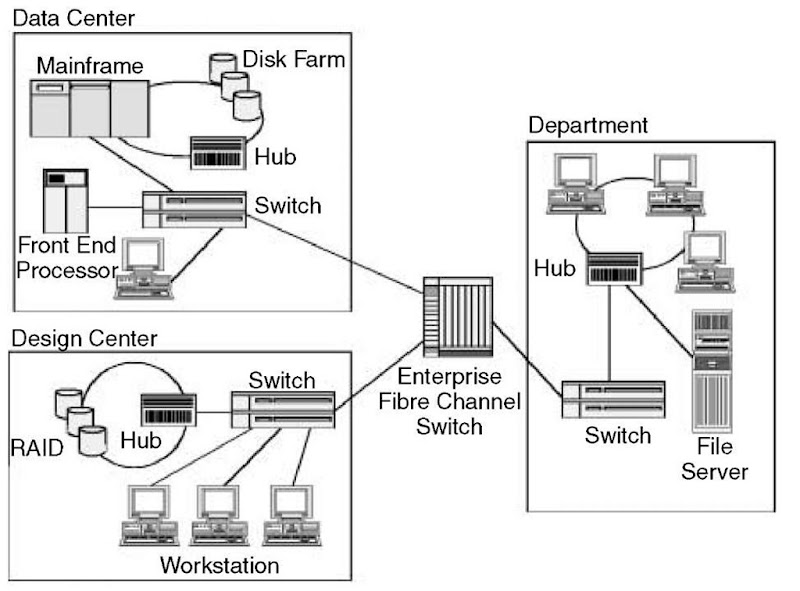
In the switched fabric topology that requires switches, all the devices are connected and communicated via switches. Fibre Channel SAN switches serve the same general purpose as any other network switches: automatically connecting senders and receivers, playing an important role in interconnecting multiple storage ports and servers. Compatible with Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP), fibre channel switches feature high-performance, low-latency, high-availability, and lossless data transmission in a Fibre Channel fabric topology and are specifically designed to handle heavy transaction loads over high-performance Fibre Channel networks.
How does Fibre Channel Switch Work?
An FC switch eliminates the need for every server to have a direct connection to every storage array and thus reduces complexity. Although Fibre Channel supports point-to-point connections in which a server physically access the attached storage directly without an FC switch, this architecture doesn't scale well. An FC switch solves this problem by acting as an intermediary between servers and storage. Servers and storage devices are both attached to an FC switch. When a server needs to access a storage device, the FC switch directs the request to the appropriate storage device.
What Is Ethernet Switch?
The word "Ethernet" is not unfamiliar to you compared with "Fibre Channel". IEEE defines Ethernet as protocol 802.3. Jargon aside, Ethernet refers to the technology of connecting computers and other devices via a protocol, which is most commonly used in wired local area networks (LANs).
When deploying an Ethernet network, Ethernet switches are indispensable certainly. Ethernet switches are the basic building blocks of networks, which bridge Ethernet devices together. Normally speaking, a LAN switch is likely to be an Ethernet-based switch with copper or optical interfaces, the port number of which vary. The speed that the switches can support may be 1GbE, 25GbE, 40GbE, 100GbE or even higher.
What Are the Differences?
As mentioned before, Fibre Channel switches are mainly used in SANs whilst Ethernet switches are mostly applied in LANs. This part will further illustrate the differences between Fibre Channel vs Ethernet Switch in four main aspects: application, reliability, transmission speed, and cost.
Fibre Channel VS Ethernet Switch:Application
Ethernet switches allow a large variety of devices to communicate with one another using Ethernet packets. Ethernet network can accommodate devices such as PCs, tablets and IoT devices. While FC switches are used only for connecting servers to storage arrays, not for general-purpose network communications, nor do FC devices require an IP address.
Fibre Channel VS Ethernet Switch: Reliability
If you are actively engaged in optic communication, you may have noticed that the fibre channel switch is lossless while Ethernet switch is risk of dropping frame. Fibre Channel is often compared to Ethernet in terms of being a lossless protocol. As for fibre channel switch, it works smoothly without dropping a single frame, and frames must be delivered in order. FC switches will send signal when they’re congesting to other devices, so these devices stop sending frames, lest the frames are dropped. This in contrast to Ethernet which will just start dropping frames when congested, relying on upper layers (like TCP) to make sure everything keeps working.
Fibre Channel VS Ethernet Switch: Transmission Speed
The maximum data rate of the fibre channel switch in the very beginning is 1 Gbps. Now it has evolved up to 128 Gbps, with 8, 16, and 32 Gbps versions still available.
The Ethernet switch transmission speed ranges from Fast Ethernet (10/100 Mbps), Gigabit Ethernet (10/100/1000Mbps), 10 Gigabit (10/100/1000/10000 Mbps) to even some 40/100 Gbps speeds. In terms of transmission speed, the Ethernet switch seems to outweigh fibre channel switch. Whereas both are in a high speed evolution.
Fibre Channel VS Ethernet Switch: Cost
Cost is also an element to be considered. In most cases, Ethernet switches are much cheaper than Fibre Channel switches. What’s more, the maintenance is also a factor that should be considered. In large IT systems, if an Ethernet switch breaks down, most admins can deal with it. However, when there is something wrong with the fibre channel switch, you need to turn to manufacturers, instead. Comparing to Ethernet switch, fibre channel switch adopts more complicated design in that it should guarantee the extremely availability of data storage, and is equipped with management function.
Conclusion
Seen from above, there are significant differences between fibre channel switch and Ethernet switch. Many Ethernet proponents may argue that Fibre Channel is dying on account of Ethernet's high-performance, simplicity, and popularity in most applications. For new network implementations, if you've not invested in FC, Ethernet networking is considered a good way to go. However, as the only long-term de facto solution for enterprise-level data storage, insisting on Fibre Channel is more persuasive. FC is a network standard to enable hosts (servers) to interconnect with storage devices. It’s completely different from Ethernet. A storage network switch is not the same as an Ethernet network switch. 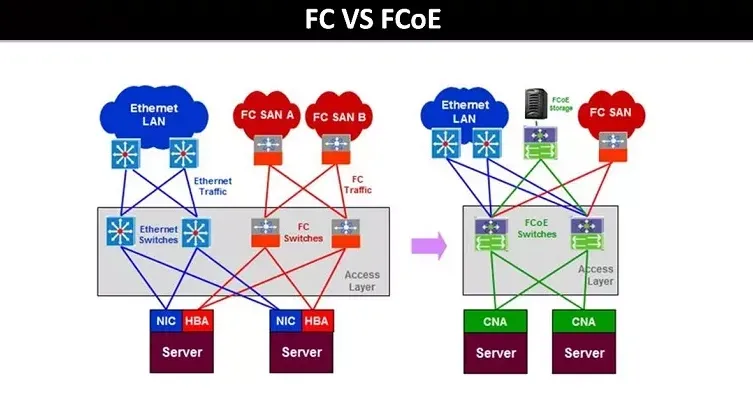 Initially, the only transmission medium of FC was fiber, but these days twisted pair copper wire is also available. That’s the opposite of Ethernet, which originally ran only on copper wires and then on fiber.An alternative form of Fibre Channel called Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) was invented to lower the cost of FC solutions by eliminating the need to purchase HBA (host bus adapter). Sticking to Fibre Channel, jumping ship for Ethernet, or picking FCoE solution all depend on your needs.
Initially, the only transmission medium of FC was fiber, but these days twisted pair copper wire is also available. That’s the opposite of Ethernet, which originally ran only on copper wires and then on fiber.An alternative form of Fibre Channel called Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) was invented to lower the cost of FC solutions by eliminating the need to purchase HBA (host bus adapter). Sticking to Fibre Channel, jumping ship for Ethernet, or picking FCoE solution all depend on your needs.