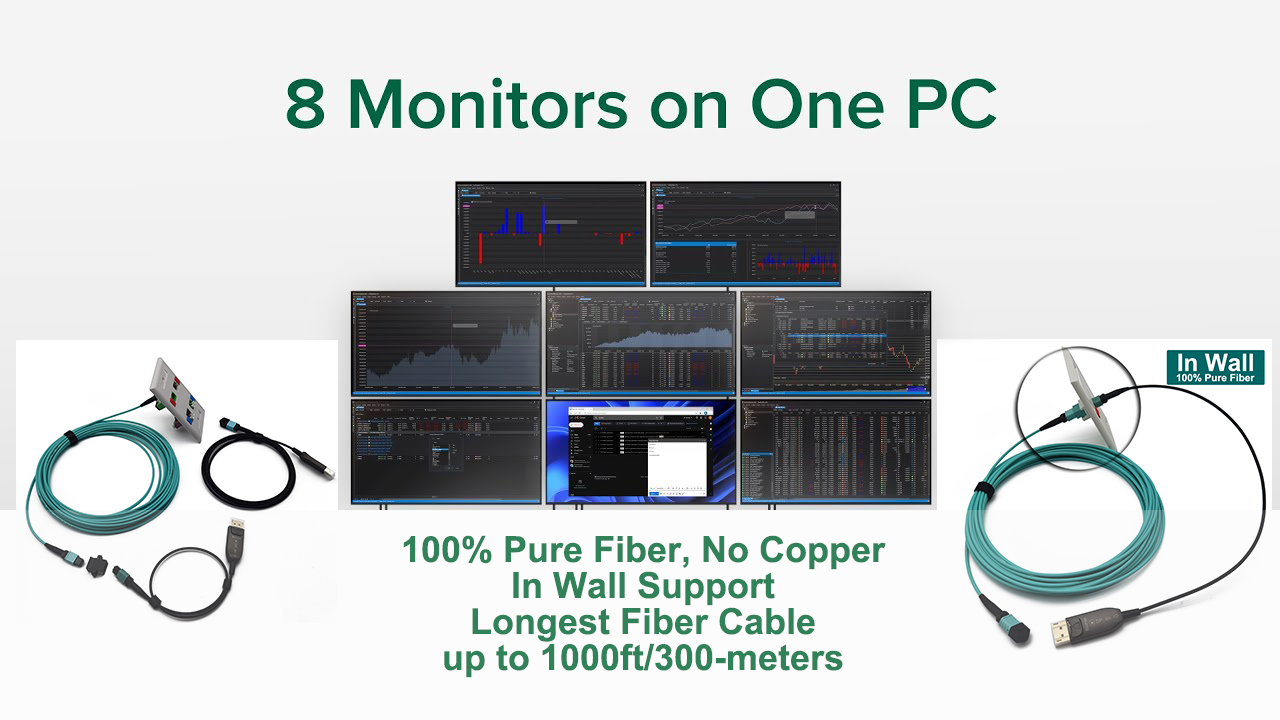
Ultimate guide to Fiber media converter
For a long time, fiber media converter is an indispensable part of the actual network set up. And it will continue to transform towards the orientation of high intelligence, high stability, easy management and low cost. Of course, selecting a right fiber media converter is also very essential to the actual applications. This article will mainly introduce some aspects to be considered when purchasing the fiber media converter.
Fiber media converter or fiber converter is a device that links two different media signals for conversion, usually exchanging the signals on a copper cable with signals on an optic fiber cable. This device is often used in MAN (metropolitan area network) access and data transport services to enterprise customers. Fiber media converter provides a balanced flow, isolation, conflict and detection of errors and other functions to ensure high security and stability of data transmission. It also breaks the restriction of the Ethernet cable length to more than one hundred meters.
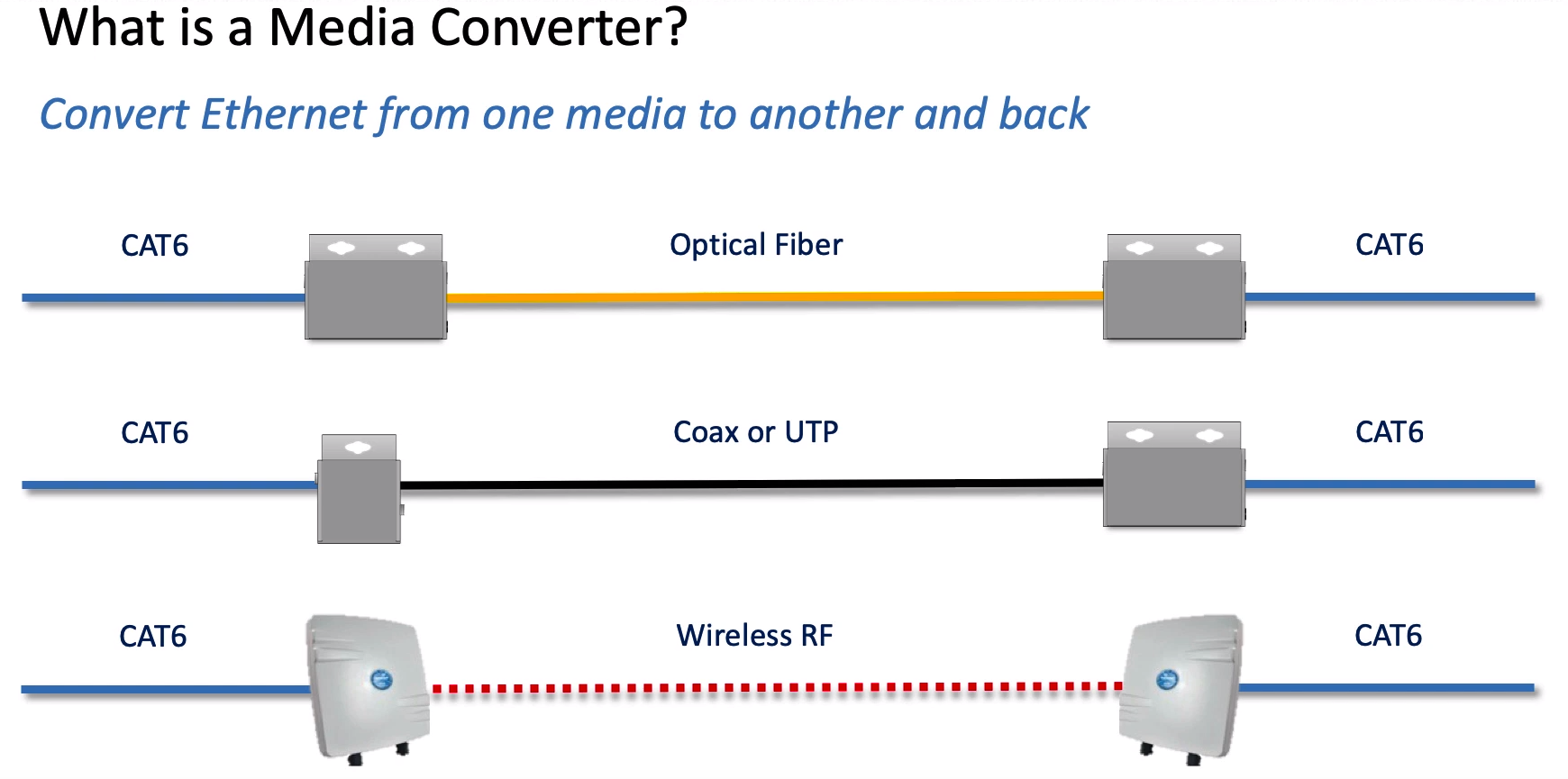
What is a Fiber Media Converter?
A media converter is a networking device that transparently converts Ethernet or other communication protocols from one cable type to another type, usually copper CATx/UTP to fiber. Media converters are often used in pairs to insert a fiber segment into copper networks to increase cabling distances and enhance immunity to electromagnetic interference. They can also extend LANs, and convert link speeds and fiber modes.
Knowing Function of Fiber Media Converter
Knowing the function of fiber media converter helps you have a better understanding of your own system which contributes to the selection process. Generally speaking, fiber media converter receives data signals from one media and converts them to another while remaining invisible to data traffic and other net devices. It supports quality of service and layer 3 switching since it has no interference with upper-level protocol information. Fiber media converter changes the format of an Ethernet-based signal on twisted pairs into a format compatible with fiber optics. At the other end of the fiber cable run, a second media converter is used to change the data back to its original format.
Fiber media converter supports full duplex Ethernet over UTP at 20 or 200 Mbps, and half-duplex Ethernet over UTP at 10 or 100 Mbps. Full duplex Ethernet is more efficient for connecting two switches or one switch to a file server. Also, fiber optic media converter can automatically sense which mode is in operation without any adjustment for mode switching.
Benefits of Media Converters
Extend LAN Distance with Fiber
Copper-based Ethernet connections are limited to a data transmission distance of 100 meters when using UTP cable. By using Ethernet to fiber conversion, you can extend link distance up to 80 kilometers or more.
Maintain Investments in Existing Equipment
Media converters enable you to migrate a local network to fiber while protecting your investment in existing copper-based hardware. This means no costly, time-consuming overhaul to your infrastructure.
Protect Data from Interference
Electromagnetic interference, or EMI, can cause corruption of data over copper-based Ethernet links. Data transmitted over fiber optic cable is completely immune to this type of noise, ensuring optimal data transmission and network performance.
Speed Conversion
Media converters allow you to convert link speeds from 10 Mbps to 100 Mbps or from 100 Mbps to 1000 Mbps.
Power over Ethernet
Power over Ethernet, or PoE, simplifies installation of Wi-Fi access point, IP cameras and more by eliminating the need for a local AC power circuit.
Types of Media Converters
Copper-to-Fiber Media Converters
Copper-to-fiber media converters enable connections of copper-based Ethernet equipment over a fiber optic link. This extends links over greater distances with fiber optic cable, protects data from noise and interference, and future-proofs a network with additional bandwidth capacity.
Discover our wide selection of copper-to-fiber media converters.
Fiber-to-Fiber Media Converters
Fiber-to-fiber media converters connect different fiber-optic networks and support conversion from one wavelength to another. They provide connectivity between single-mode and multimode fiber, as well as between dual and single fibre.
PoE Media Converters
Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) media converters provide reliable and cost-effective fiber distance extension to PoE-powered devices. PoE media converters can power devices like IP phones, video conferencing equipment, IP cameras and Wi-Fi devices over copper UTP cabling.
Stand-Alone vs. Chassis-Based Media Converters
Stand-alone media converters are compact and can be AC or DC powered. They are commonly used to convert one copper link to fibre in point-to-point installs. These converters are easy to deploy and offer a range of useful functionality for your network, such as auto-MDI/MDIX, link fault pass through and more.
Chassis-based media converters are used in high-density locations such as a data center or equipment room. They mount in racks alongside network switches, enabling the conversion of copper ports on legacy switches to fiber.
Managed vs. Unmanaged Media Converters
Managed media converters give network administrators complete control of data, bandwidth, and traffic. This lets admins manage and troubleshoot a network remotely and securely to achieve and maintain optimal performance and reliability. Thus, these converters are most suitable for environments requiring a medium- to large-scale deployment of media converters.
Unmanaged media converters are "plug-and-play" converters which are easy to install and troubleshoot. Unlike managed converters, these do not provide the same level of monitoring, fault detection, and configuration.
Commercial vs. Industrial Media Converters
Commercial media converters are designed for typical office and data center environments where ambient temperature is controlled. These converters provide a cost-effective way to extend the distance of your network and improve the life of copper-based equipment. They are perfect for commercial applications that do not deal with extreme environmental issues.
Industrial media converters convert data between twisted-pair cabling and multimode or single-mode fiber optic cabling, extending the distance of a network. They are able to withstand extreme temperatures (-40°C to 75°C) and harsh conditions, feature redundant power design and are designed for high shock and vibration locations. This makes them a perfect fit for industrial networks. Industrial media converters are commonly used in applications such as building automation, oil and gas drilling and mining.
Applications and Use Cases for Media Converters
Enterprise
PoE media converters backhaul Wi-Fi data and power access points, improving network functionality and reliability in commercial applications.
Security and Surveillance
PoE+ simplifies installation of IP security cameras by eliminating the need for a power circuit near the installed device. PoE+ media converters power these devices and backhaul signals to remote data centers or operations centers.
Government and Defense
Media converters provide secure, high-performance LAN connections from the data center to desktops with fiber. Highly reliable with unsurpassed bandwidth, speed and security, fiber to the desktop is a perfect fit for government and defense applications.
Fiber Mode Conversion
Never worry about varying fiber types in your application again. Convert fiber links from multimode to single-mode and vice versa with media converters.
Other Factors to Consider During Your Selection
Here are some factors that you can consider when purchasing a fiber media converter:
First, according to different data rates, there are various fiber media converters to match the transmission speeds. Thus, data rates should be considered as an important factor.
Second, figure out what transmission media are in your network, and find the corresponding cable types. For instance, there are fiber to copper, single-mode fiber to multimode fiber, dual strand to single strand and so on.
Third, diverse fiber media converters have different port types. Typically, there are two types of ports, one for copper and the other for fiber. The copper ports are all designed for RJ45 copper cables. But in terms of fiber ports, there are also another two types. One is designed for fiber optic transceivers (SFP, XFP, etc), and the other for fiber optic patch cables (SC, LC, etc).
Fourth, transmission distances of fiber media converters are varied to satisfy different length demands.
Fifth, if main power is not available or difficult to deliver in physical locations, PoE fiber media converter can be an option to supply the required power.
Sixth, different power supplies are also available. For example, AC (alternating current) power supply, DC (direct current) power supply, internal power supply and external power supply are the common choices.
Applications
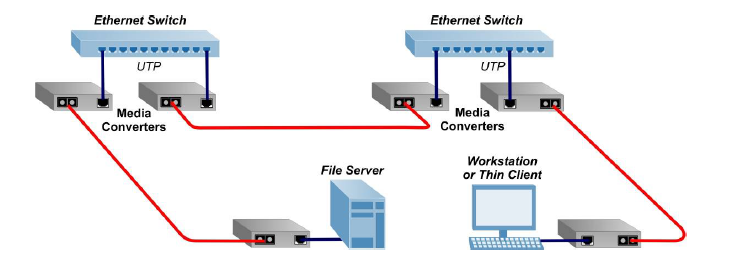
Fiber optic converters can be used in lots of applications. Here are some examples. Point to point application can connect two UTP Ethernet switches (or routers, servers, hubs, etc.) via fiber, or to connect UTP devices to workstations and file servers.
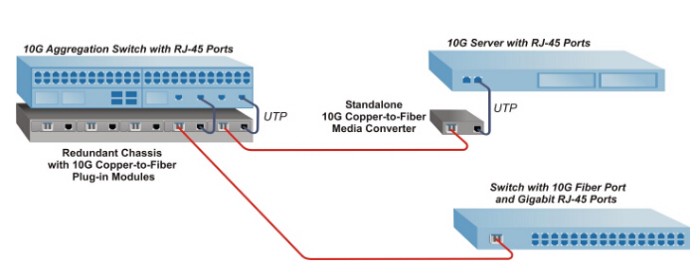
10G Ethernet application extends distances between 10G switches and servers.
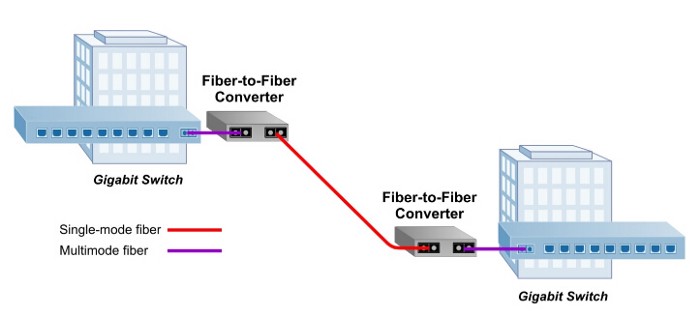
Multimode to single-mode application extends a multimode network across single-mode fiber with distances up to 160 km.
Conclusion
Media converters can be used anywhere in the network to integrate newer technology with existing equipment to support new applications, technologies, and future growth.Before you select a media converter, you must consider your current and future network requirements.