How to do DDM Digital Diagnostic Monitoring
What is DDM in Transceivers?
DDM stands for Digital Diagnostic Monitoring according to the industry standard MSA (Multi-Source Agreement). DDM is also commonly known as DOM which stands for Digital Optical Monitoring. When purchasing a transceiver today you are given the option with or without DDM/DOM. Most of the transceivers in use today feature the DDM function. DDM is a technology that allows users to monitor parameters of the fiber optic transceivers in real time.
What does DDM do?
DDM enables the users to monitor key parameters that can affect the performance of a fiber optic transceiver such as:
- Transceiver temperature
- Transceiver supply voltage
- Laser bias current
- Transmit average optical power
- Received optical modulation amplitude (OMA) or Average Optical Power
The real time monitoring of these parameters can alert the system when a transceiver is functioning abnormally or when specified operating limits are exceeded. The DDM function can be used to isolate the particular location of a fault within a fiber optic network system as well. In addition to isolating faults, the DDM can also aid in predicting failures on fiber optic links based on the transceiver performance. The DDM function allows users to be more proactive when maintaining their network and also helps to ensure minimal disruption. DDM allows network managers to find potential failures before system performance is affected. DDM’s failure notice system also allows network managers to switch to a backup link or replace a device functioning abnormally. DDM also serves to verify the module’s compatibility.
How to do DDM Digital Diagnostic Monitoring ?
Modern optical transceivers support standard digital diagnostics monitoring (DDM) functions, which enable real-time monitoring of modules’ parameters. And the DDM information of the modules is commonly read via Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
After enabling the DDM function of transceivers, the Net-SNMP (snmpwalk) tool is typically used to poll the information.
Sample for Net-SNMP tool: Take the Cisco ASR9k as example. We want to read the optical Tx/Rx power of the module via SNMP. The ASR9k is IOS-XR, Version 5.3.1. The MIB is “CISCO-ENTITY-SENSOR-MIB” and the OID is 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.9.91.1.1.1.1. So the command by using Net-SNMP tool is like:

Then the CLI will show the output of celsius/amperes/mWatts/voltsDC sensors, and you just have index to the particular sensor you need.

Note: Ensure the Package Installation Envelopes (PIE) are loaded before polling. The optical power will not be presented as “dBm” but as “mW”. To convert mWatts to dBm with the formula 10*log(mW) = dBm.
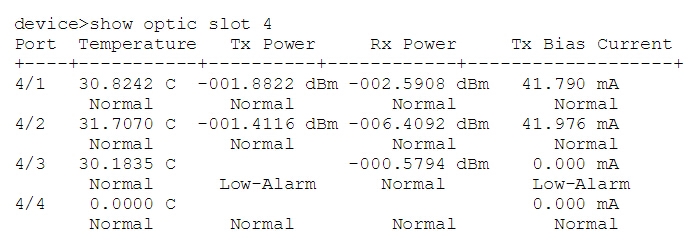
Since there are different SNMP equipment vendors, there will be some difference in MIB and OIDs. And some devices are able to show the DDM information by only using some simple command like show optic port-number to get the result of single transceiver:
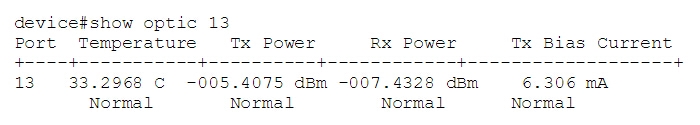
or by using show optic slot slot-number to get all optics in a particular slot.