Is HDMI Over IP Right for Your AV System?
First introduced in 2002, the High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is now the connection standard for digitally transferring video and audio from its source to a video display device. HDMI has developed several versions since its inception; one of the newer iterations is HDMI over IP.
This article introduces HDMI over IP technology.
What is HDMI over IP ?
Are you familiar with "HDMI over IP" or "AV over IP" in recent years? What it is all about?
It is a transmission technology that processes (compress/ uncompress) signals and transfers them over a network.
With this technology, you can integrate multiple network devices and manage them without geographical limits. HDMI over IP is already around you. You can find its applications in daily life, such as streaming, broadcasting, and more.
However, another argument in recent years is how this technology can be applied to the professional audio and video market and need to be considered in your next project.
Traditional System Structure VS HDMI over IP:
What's the Difference?
Firstly, we have to clarify the differences between traditional HDMI and HDMI over IP. Both systems may seem similar at first glance, but they're different in many ways.
We can explore two aspects.
- System Infrastructure
- Functionality
System Infrastructure
Both matric systems achieve the same goal but in a different layout.
A traditional AV system will require:
- Source: Devices like NVRs, Blu-ray DVD players, PC, and HDMI cameras.
- Transmitter: Processing signal and sending it to the remote end.
- Receiver: Receiving a signal from the local end and sending it to a display.
- Display: Devices like TVs, LCD monitors, and projects for display video sources.
An HDMI over IP system will require:
- Source
- Encoder: It can convert an AV source into chunks of digital data called packets and send them through a network.
- Decoder: It can convert packets back to an AV signal and send them to a destination.
- Ethernet Switch/ Network Switch: It can organize Ethernet devices and use packet switching to send packets from one/ multiple sources to different destinations.
- Display
Functionality
In the traditional AV system, each device is designated for a specific function, such as an extender for signal extension, and a switcher for signal switching, but in the AV over IP system, all functions are combined into encoders and decoders.
1. Extension
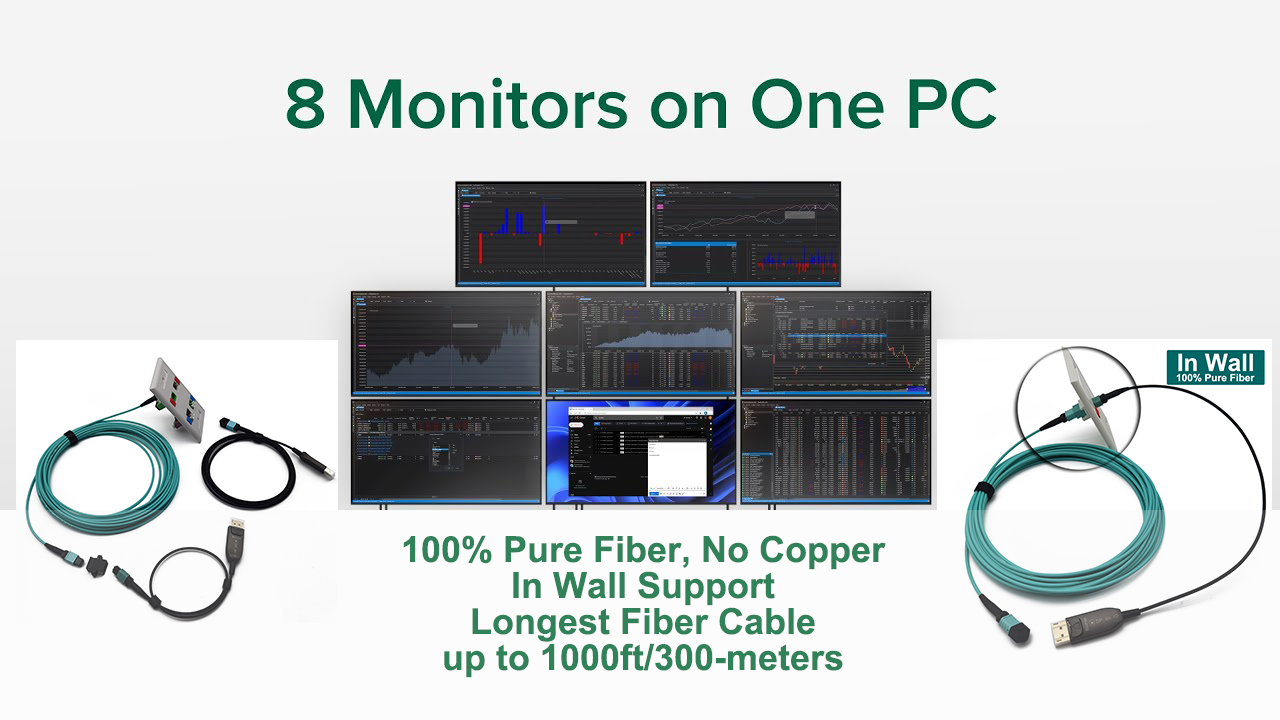
Every end-point between an encoder, a decoder, or an Ethernet switch can be 100 meters (300 feet) apart.
2. Distribution
Use an encoder, an Ethernet switch, and multiple decoders to distribute an HDMI signal.
3. Switch
Use multiple encoders, an Ethernet switch, and a decoder to switch multiple HDMI signals.
4. Routing
Use multiple encoders and decoders thru an Ethernet switch to route various HDMI signals.
Why use HDMI over IP ?
It is used in various applications such as department stores, sports bars, restaurants, churches, control centers, classrooms, hospitals, etc. Here are four of the primary reasons to use this technology:
- Distance: With the use of AV devices such as HDMI extender transmitters and receivers, network switches (which can be “daisy-chained”), and fiber, long distances can be reached.
- Scalability: Adaptability is crucial for any AV system. The need for system changes and improvement is inevitable over time. With HDMI over IP, all you need to upgrade is an additional encoder and decoder.
- Cost-effective: Nowadays, most enterprises have existing network infrastructures. You can easily integrate Ethernet devices into the existing network instead of building a new one. The high scalability of HDMI over IP may also save you some costs shortly from re-cabling and upgrading devices.
- Flexible Controls: Due to the flexibility of Ethernet. Every device within the network can be controlled via not only a keyboard and a mouse but also PC software and a mobile APP. This feature gives users access to intuitively control a large-scale AV system without getting confused by a vast amount of inputs and outputs.
Conclusion
Ethernet or IP technology brings opportunities to every corner of the world. The professional audio and video industry is no exception. Building your AV system over IP allows you to integrate multiple AV devices, expand the system when needed, and gain more intuitive control of complex systems. Still, in addition to all the benefits, we should be wary of network security and the cost of initial setup to get the best results for your project.