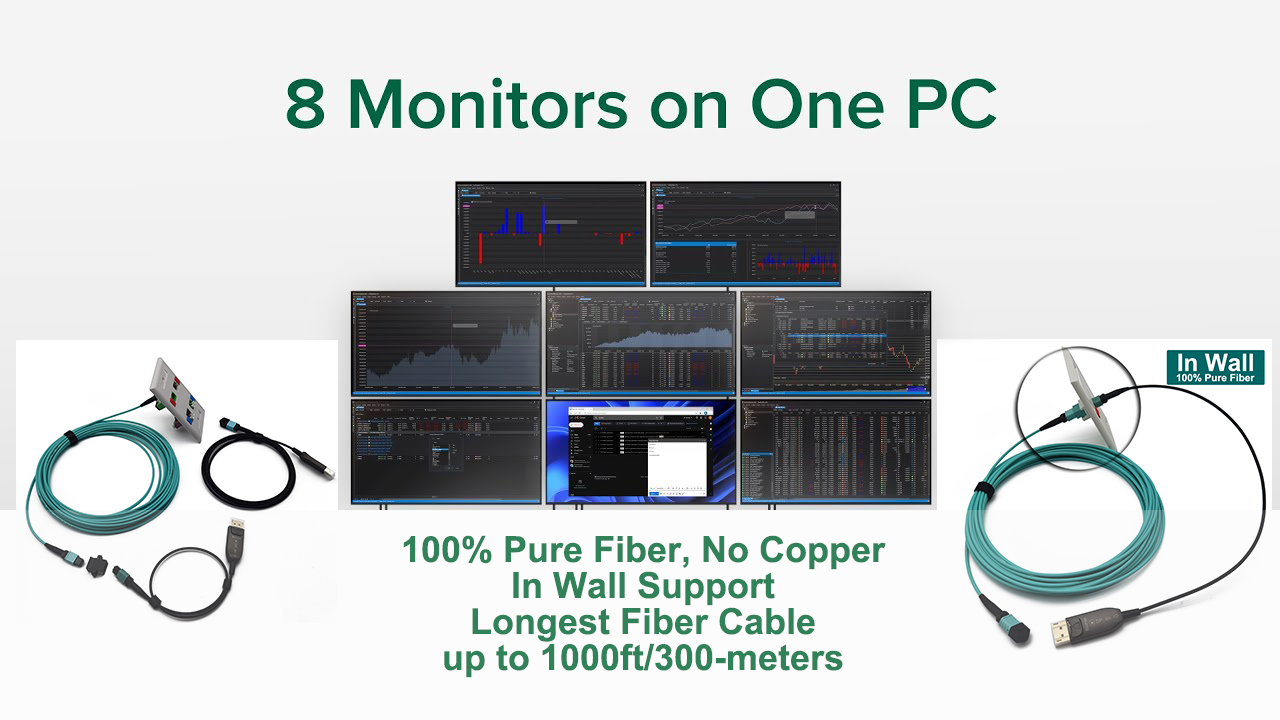
Fiber Optic Modem Guide
Fiber optic modems (or FOMs) connect electronic devices, such as computers, to a network or the Internet, providing electrical-to-optical conversion of electronic communications and data signals for transmission using tactical fiber optic cable assemblies. As these fiber optic modems are becoming more and more popular, it is important to know about them before blindly using them. This article gives you an in-depth look at these fiber optic modems and how they work.
How Does Fiber Optic Modem Work?
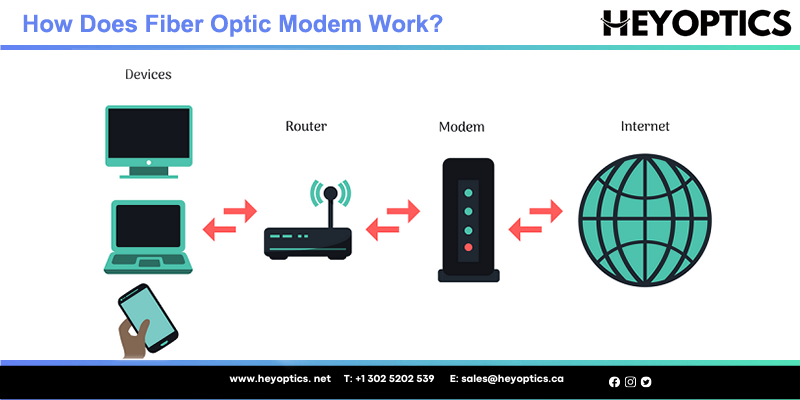
Fiber optic modems receive incoming optical signals over fiber optic cables and convert them back to their original electronic form for full duplex transmission. Together with the tactical fiber optic cables, the FOM provides a rugged, secure, and easy deployable optical link.
- The internet signal transmitted via fiber optic cables to the fiber optic modems.
- The modem transforms the internet signals into electronic data.
- This transmission is a full-duplex transmission. That means the data can be transmitted from the internet source to the electronic device and vice versa.
What are the Types of Fiber Optic Modems (FOM)?
There are different categories of fiber optic modems according to the data transmission protocol followed by the modem. Let us discuss the types of FOM in brief.
- E1 FOM: The E1 FOMs are the modems that act according to E1 data transmission standards. These modems can be used for single or multiple fiber optics data transmission channels. These modems are suitable for multichannel, simultaneous, time-division multiplexing. The most appreciated use of E1 FOMs is international telecommunication. It can be used for LAN, WAN, MUX, and router-based networks.
- V35 FOM: V35 FOM is utilized for single or multimode transformation and transmission of electrical-optical-electrical signals. This V35 modem acts as electrical to optical data converter and vice versa at the end of the fiber optic cable. The transmission range of these modems is up to 100km.
- RS FOM: RS stands for recommended standards. The modems that act under recommended standards are called RS modems. These RS standards are established by The Electronics Industry Association. The different RS FOMs available in the market are as follows.
- RS232: RS232 is the most basic fiber optics modem. It is a single-mode modem, therefore only one receiver and one transmitter can be connected. It offers 20K bits per second data transmission rate.
- RS422: RS422 FOMs are designed for faster data transmission rates and longer transmission distance. They can transmit up to 20km at 10MBPS transmission rate.
- RS485: RS485 FOM is designed for multimode data transmission. For multichannel fiber optic transmission, these RS485 fiber optic modems are used. It supports over 32 channel simultaneous transmission.
What is the maximum distance that a fiber optic modem can go?
The maximum distance a modem can go is the difference between receiver sensitivity and transmit power of the fiber optic modem, divided by the transmission loss of the fiber used. For example, a basic single-mode OSD815 digital video system’s transmitter power is greater than -10dBm and its receiver sensitivity is better than -29dBm so the difference of 19dB at 1310nm allows operation over at least 45km. Note this would be very poor design because there is no allowance for a link margin.
Which are the Advanced Applications of Fiber Optic Modems?
Fiber optic modems (FOM) are nowadays being used in several applications such as data communication network systems, inter-network communication systems, and so on. They can be used to expand networks across cities and states, and help you extend the distance by around 100km, without compromising on speed and signal strength. This is why they are useful in networks of mission critical applications such as defense and government. Here are some advanced applications of fiber optic modems:
- Smart homes
- IoT
- Augmented and virtual reality
- Cryptography
- High speed device linking and syncing
- Microwave extension linking
- Satellite downlinks
- System integration of public and private networks
What are the Features of Fiber Optic Compatible Modems?
That Make Them Popular FOMs are gaining popularity over DSL modems and cable transmission due to their beneficial features. The fiber optic modems offer the following benefits.
- This type of modem is immune to electromagnetic interference.
- This system is immune to data loss; therefore, the user gets uninterrupted data transmission.
- These modems are absolutely compatible with the single or multi-portal transmission.
- Due to uninterrupted data transmission, these modems can be used for long-distance telephone communication. As these modems can resist electromagnetic interference, thus, the audio signal transmission is clear.
- Having Fiber optic as transmission media, the speed of transmission is higher than the general cabled network. Also, in comparison to a wireless network, the function of these fiber optics modems is not affected by harsh weather fluctuations.
- They are microprocessor based and using ANSI certified ones is highly recommended.
- These modems have a user friendly GUI and multiple features such as fiber path protection, menu-based interface and control, end-to-end monitoring controls which allow handshaking of devices, and smart manager.
- They can be used as a standalone device or mounted on a rack in an integrated network.
- They have self-troubleshooting features such as remote loopback as well as local capabilities.
- You can use NDT or non-intrusive testing techniques such as BERT to check the communication link of these modems. This prevents closure of systems when testing.
- They support various encryption product lines.
- They can pass bipolar violations, and offer full modem redundancy.
- They help reduce latency of the legacy networks and offer a huge bandwidth even for VoIP calling, video conferencing, archiving of bulky files, and so on.
- Overall, fiber optics along with these modems and other network devices offer your business network enough scalability, thus leaving room for future expansions, configuration changes, and application flexibility.
Conclusion
Fiber-optic modems are ideal for handling large amounts of data. Optical fibers allow data to be transmitted quickly and efficiently. Available in single-mode or multi-mode models, it is important to choose the one that best suits your needs.
If you're a business owner looking to expand your network, opting for a hybrid network can be helpful as it allows you to keep your old network and connect it with fiber. This increases speed, signal strength and distance, and is relatively affordable. However, in order to take advantage of the benefits of fiber modems, you must buy from a trusted supplier.