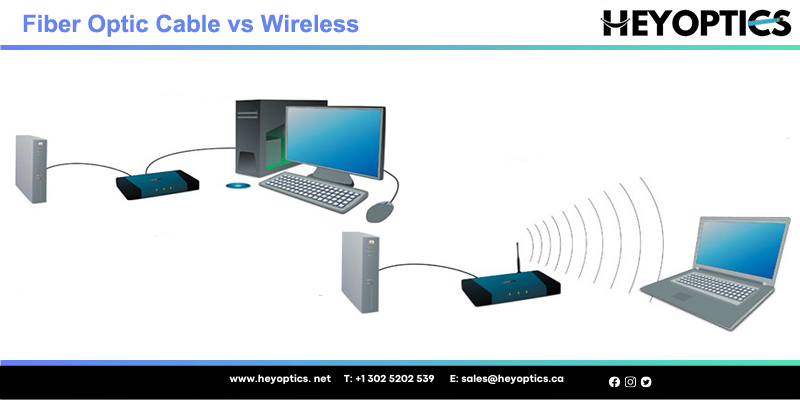
With the rapid development of science and technology, most people can access the Internet. Our home and business networks rely on wired or wireless technology. Wireless communication technology is also seen as a modern alternative to traditional wired networks. When both sides: fiber optic cable and wireless are opposites in the competition, who will win the favor?
If you want to understand the basic difference between Fiber Optic and Wireless Broadband technologies then you don’t need to bother much because the difference is quite simple and uncomplicated. As the name itself suggests, Fiber-optic cable technology mainly works via the use of cables converting data transmission which includes images, text, video, and emails into a torrent of light and this flood of light passes via cable, it is changed back to its original form. On the other hand, wireless broadband converts the data transmission into electromagnetic waves for broadcasting.
![]()
What Is Fiber?
It is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of light through an optical fiber. It is delivered through thin glass pipes known as fiber optic cable with the usage of light waves. This technology is generally considered the successor to DSL broadband which is delivered over a copper telephone network.
What Is Wireless?
The wireless network is a network set up by using radio signal frequency to communicate among computers and other network devices. Sometimes it is also referred to as WiFi network or WLAN. This network is getting popular nowadays with the feature of easy setup and no cabling involvement. You can connect computers anywhere in your home without the need for wires.
Fiber Optic Cable vs Wireless
Below is a side-by-side comparison of the two technologies, so it is easier for you to understand which one is a better option for you.
| Fiber Optic |
Wireless Broadband Connection |
| The Fibre-optic connection is built around the fiber optics, which uses light to transmit the data. |
The Wireless broadband connection works by converting the data packets into electromagnetic waves to broadcast them on a specific channel. |
| Fiber optic provides the same speed, but the way fiber optic handles the network congestion and provides high speed makes it a better option when a single network is handling many users. |
With a wireless connection, you will face network congestion that causes slow load times. |
| Fiber optic connection's speed and network stability don't degrade proportionally with distance. |
The distance can sometimes hamper the speed of your network when you are working with a wireless connection. |
| Fiber optic cables have been installed in urban and metro cities. But if you are living in the countryside, it will take some time or even years for you to get a reliable connection. |
On the other hand, a wireless connection theoretically can be installed anywhere in the world. |
| The cost of laying down a fiber optic is quite expensive, and it could take months before you could make a connection with the Internet. |
One of the biggest advantages of a wireless connection is that it is cost-effective in many ways. Wireless broadband services can even provide internet connectivity in the remotest areas. |
| If a fiber optic is broken, the cost of replacing that part can be quite high. |
The installation process is quite easy, and within a day or two of applying, you will get it installed in your office or home. |
| Lastly, the fiber optic connection works with a specific set of hardware, and that also comes at a cost that some people might not be comfortable investing in. |
No need to buy expensive hardware to get connected to the internet. A wireless connection works with all network hardware, no matter what they cost. |
To understand the other differences, just go through the below-mentioned factors:
- Speed: If you think that a wireless network transmits data at the same rate as a fiber optic cable does then you are wrong. If you find the difference in speed in both the networks, you will find that fiber optic provides a much higher speed than a wireless network. For example, the wireless network becomes quite slow during peak hours because all users of wireless network start sharing the same network and its bandwidth. Due to the congestion of the network, the wireless connection becomes slower whereas fiber optic network does not get affected in such situation. The connection speed remains good even during peak hours.
- Distance: The signal with a wireless connection gets degraded with distance. You must ,have noticed that wireless connection is only meant for a limited area because when you go far away from the signal range or modem, you start losing network or start experiencing fluctuation in the signal. But in terms of cost, wthe ireless connection is quite cheaper than fiber optic. The cost ofiber-opticptic connection is so high in those areas where internet service providers need to lay down the fiber optic cable to provide you the connection. In that manner, the connection becomes quite expensive and it is not a wise call to get this connection at a higher rate then.
- Mobility and Convenience: Today people need more freedom and comfort to enjoy life. Similarly, when it comes to getting an internet connection, they all want a modem or device which they can carry here and there without any trouble. When internet has become an essential part in today’s life, no one wants to disconnect themselves from the web world. Therefore portable devices are there to provide web access to the users anywhere anytime. While you are moving or traveling, wthe ireless device is quite handy in accessing the web world. Similarly, when you check-in in many hotels, coffee shops, and restaurants, you don’t need to ask for an internet wire, you just need to get connected to a wireless network of these places to enjoy web access. However, there are many areas in India where wireless network is so weak or not wthe orking. In this case, you need a fixed-line connection to access the web world.
If you look the difference carefat ully between these two technologies, you will find both pros and cons in each of the technologies. Many times, having a wireless network is quite handy and sometimes, a fixed-line connection like fiber optic can fulfill your need. If you don’t any issue with paying little more on the connection then it is a better call to go for a fiber optic network over a wireless network. Before getting this connection, check whether it already exist in your area or not because getting a new connection or installing the same network may cost you quite much.
Pros and Cons of Fiber Internet
Fiber Internet is the wired choice of our present times. It has replaced traditional copper-based facilities such as T-1, DSL, and Ethernet over Copper. With high speeds and extremely reliable service, we have found that our customers are only choosing copper when the fiber isn't available or too expensive to obtain.
Pro1: Connection Quality
The top benefit of fiber optic Internet is the quality of your connection. Unlike other wired connections, and especially wireless, fiber’s signal barely degrades the further it moves from the source of the connection. For example, copper has a distance limitation that can't even be addressed adequately with repeaters. At a certain distance, you simply run out of signal.
Additionally, fiber has a significantly higher resistance to electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio-frequency interference (RFI), meaning the signal won’t be disturbed by things that carry an electrical signal, like power lines or your building’s physical infrastructure.
Since environmental factors have little effect on fiber, it can reach speeds anywhere from 50 Mbps to 100Gbps. This speed is unmatched by competing technologies.
Pro2: Security
Another advantage of fiber is its ability to maintain a more secure network. With DDoS attacks on the rise, it’s essential to keep your business safe in any manner possible. The only way to disrupt fiber-optic Internet is to cut a cable. If a fiber cable is compromised, the entire system is impacted due to a disrupted signal, allowing you to identify breaches more rapidly and react accordingly. This is as opposed to copper circuits which can be tapped and data can be intercepted without you knowing it.
Since there are no signals radiated externally from the cable, it also makes it impossible for others to “listen in” on your transmission, further securing your network.
Pro3: Scalability
Optical fibers are five times smaller and twenty times lighter than copper wires making them easier to install than other options. They also allow for easy upgrades of equipment since new cables can be laid over the original fiber. This makes it a great solution for growing businesses or those looking for network expansion.
Since fibers can be turned on or off as required, businesses can install fiber optic cables in preparation for future growth and route their service until it’s required.
Pro4: Overall Cost
While the initial cost may be higher (more on this later), the overall cost of using fiber-optic Internet is lower than other methods.
Fiber cables require fewer maintenance costs as they’re resistant to corrosion, making their connection much more reliable. This makes them the leading option in areas where other wires may be exposed to elements and require replacement over time.
Con1: Risk of Damage
While there are benefits of fiber optic cables being light and thin, they're at a higher risk of physical damage. If unprotected, it is significantly easier to damage these cables during rewiring or renovations to your infrastructure. It’s important to hire companies that understand how to work with fiber cables when installation as cables can be damaged, especially around corners.
The higher risk of these cables being physically damaged also leads to the potential of more people being affected. Since more employees are using the same cable, an outage could lead to a larger disruption in productivity throughout your business.
Con2: Initial Cost
With lower overall costs, compared to other traditional methods of connectivity, there’s still an initial setup cost that may raise some red flags with your CFO. Along with the cost of the cables comes the installation fees, permits, the connection nexuses and fiber endpoints, as we, ll as the specialized tools for sea tup and testing. Many of these costs can be mitigated or dropped completely if your building is already wired for fiber.
Pros and Cons of Wireless Internet
Wireless, whether is uses licensed or unlicensed spectrum, has been around for years. I first set up a customer with a wireless connection to the Internet in 1998! The technology has progressed dramatically since that time and bandwidth of 1000 Mbps or more is possible, at short distances. It provides a low-cost entry to getting your company on a network and the freedom to move about, but its limited bandwidth and security risks may be enough to point you in another direction.
Pro1: Initial Cost
Wireless networks offer a solution to fiber-optic’s high initial cost in places where fiber is not already built out. Much of the installation fees are diminished as wireless networks don’t require as extensive an operation as fiber. For a short-term fix, wireless could be the best option for your company. You'd only need an antenna and network access that the antenna connects to.
Pro2: Quick Installation
With wireless Internet connectivity, it is possible to setup a connection in a day, if an antenna is available. There is no digging required and no reliance on a third party such as the phone company or a fiber carrier. I had a customer in a downtown Washington DC townhouse that we set up on a 100 Mbps wireless connection in less than a week.
Pro3: Hot Spots
Depending on your type of business, having the ability for customers to access hot spots within your network could be a great benefit. This could be separate from the network your employees use, providing set up more security for your internal use.
Con1: Signal Strength
One of the largest issues with wireless Internet is that signal strength degrades the further you move from a broadcast station. Fiber optics mitigate this through a wired network, but wireless, even at its best, isn’t able to provide the same high speeds to your company.
Con2: Security
Maintaining security with wireless networks is far more demanding than with a fiber-optic network. Where a fiber optic cable must be cut for access, anyone with the right skills can access a wireless network. There are also limited ways for them to be tracked. It's harder to crack when using licensed spectrum, but with wi-fi, security risks may result in use just for general use transmission rather than data that really should be protected from compromise.
Conclusion
Every coin has two sides. As with fiber optic cables and wireless, network connections are no exception. A wired connection will provide higher reliability and less chance of interference. And wireless connectivity will provide greater flexibility and the ability to easily add devices to the network.
The wireless network is a great backup solution in case your fiber optic Internet goes down. The two can, and should, complement each other, providing the speed and reliability of fiber, with the mobility of wireless. It also has utility for rural locations where it is prohibitively expensive to run fiber. If transmitting any kind of sensitive data, it is available to use licensed spectrum so you're not using public frequencies, which are vulnerable to compromise.
For those in an urban area, where fiber optic cables have, more than likely, already been run, consider adding them to your infrastructure and making use of the fastest Internet speeds on the market.